Aims: To analyse the changes in endothelial cell density (ECD) after pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) and to identify the factors implicated.
Patients and Methods: This was a prospective, consecutive, and non-randomised, case-control study. All 23-gauge vitrectomies were performed by a single surgeon at a tertiary centre. ECD was measured at baseline before surgery and on postoperative Days 30, 90, and 180. The fellow eye was used as the control eye. The primary outcome was a change in ECD after PPV.
Results: Seventeen patients were included in this study. The mean age of the patients was 65 years. The mean ECD count at baseline was 2340 cells/mm2.
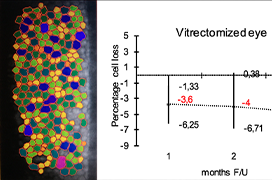
The median ECD loss in the vitrectomised eye was 3.6%, 4.0%, and 4.7% at Days 30, 90, and 180, respectively, compared to +1.94%, +0.75%, +1.01%, respectively, in the control eye. The relative risk of ECD loss after PPV was 2.48 (C.I. 1.05–5.85, p = 0.0247). The pseudophakic eyes lost more ECD than the phakic eyes, but this was not statistically significant. There were no significant differences in diagnosis, age, surgical time, or tamponade used after surgery.
Conclusions: Routine pars plana vitrectomy had an impact on the corneal endothelial cells until Day 180 post-op. The phakic status was slightly protective against ECD loss after PPV, although it was not statistically significant. The pathophysiology of corneal cell damage after routine PPV remains unclear. Further studies are required to confirm these findings.