Aid: Familiarize themselves with the operating techniques in their own modulation to solve hypotropic states with elevation or hypotropic states with depression.
Methods: Surgery technique “cul-de-sac” is a procedure with fixed adjustable sutures (non-absorbable suture), which are guided in parallel on both peaks original insertion of inferior rectus muscle. The node itself of suture is done in cutting the muscle and through the original insertion only leads arc suture. During „counterclockwise transposition“ procedure sec. Knapp, the horizontal rectus muscles are fixed at the straight inferior rectus muscle level. The author included their graphical diagrams.
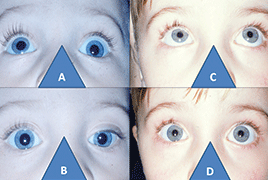
Material: At the Department of Ophthalmology in the Faculty Hospital Královské Vinohrady in Prague (Czech Republic, EU) in the years 1996 - 2014 a release relaxing operation of the inferior rectus musle by the technique “cul-de-sac” on 49 eyes. Indication was double elevator palsy in 31 patients, congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles in 15 patients and in 3 cases, it was thyroid eye disease. “Counterclockwise transposition” procedure sec. Knapp was indicated twice for paresis of the inferior rectus muscle in 2015 and 2016. For the first time, it was a congenital form. It was detected histologically atrophy of stripped muscle with hypertrophy collagen. The second traumatic form was formed after an orbital injury.
Results: We provided adequate relaxation of the inferior rectus muscle and practical restoration of eye elevation by the technique “cul-de-sac“ in 18 preschool children with the double elevator palsy and three adult patients with thyreiod eye disease. We had to restore motility to complete the procedure by classical transposition procedure sec. Knapp of both horizontal rectus muscles to the direct superior rectus muscle in elderly children and adults with the double elevator palsy, as well as in all patients with the congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles. Indicate the inclusion of this transposition influenced the degree of fibrotic rectus inferior muscle given by age. “Counterclockwise transposition“ procedure sec. Knapp ensured the practical disappearance hypertropie in both cases of paresis of the inferior rectus muscle. The alignment of the position of the eyes without diplopia in the direct view was ensured by prismatic correction.
Conclusions: To release the fibrotically altered inferior rectus muscle in the double elevator palsy, the congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles and the thyroid eye disease, the operation of adjustable sutures was necessary in accordance with our experience with the technigue “cul-de-sac“ in its own modification. The transposition procedure sec. Knapp, either classical or “”counterclockwise” “ in its own modification, was of paramount importance for the solution of the vertical deviation of a paretic ethiology.