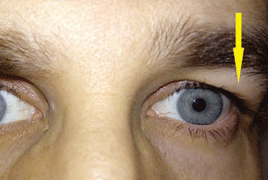
Silent sinus syndrom is rare and slow progressive disorder associated with asymptomatic chronic maxillary sinusitis and collapse of the orbital floor. The most common manifestations are enophtalmos, hypoglobus and pseudoretraction upper eyelid. Silent sinus syndrome is almost a unilateral condition and is usually diagnosed in patients in their 30´s and 40´s. The largest risk factors is underlaying aberrant nasal anatomy. The subsequent osteomeatal complex obstruction leads to hypoventilation of the maxillary sinus and negative pressure development. The sinus cavity is filed with a combination of mucus and acellular transudate. This proces create a chronic mucosal inflammation with demineralization and collapse of the orbital floor. CT imaging is pathognomonic and shows ipsilateral maxilar sinusitis and the orbital floor is inferiorly displaced. The differential diagnosis includes chronic sinusitis, osteomyelitis, malignat sinus infiltration and orbital trauma. The endoscopic antrostomy is the gold standard to re-establish normal sinus aeration. In this article we describe patient with silent sinus syndrome, who has been treated at our clinic and his symptoms were corrected ad integrum after the surgery.
- Virtiol – Simulation of Quality of Vision with Multifocal and Edof Intraocular Lenses
- Corticosteroid Induced Posterior Subcapsular Cataract
- Ocular Manifestations in Patients with HIV infection
- The Importance of Evaluating the Development of Oct Findings During Conservative Treatment of Vitreomacular Traction Complicated by Macular Hole Formation
- Silent Sinus Syndrome
- Idiopathic Chodoidal Neovascular Membrane in a 12-year-old Girl
- Screening, Treatment and Long-term Observation of Retinopathy of Prematurely Born Children in the Czech Republic