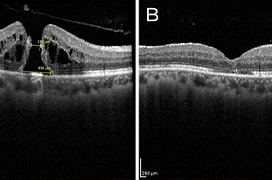
Aim: The main aim of this study is to evaluate the anatomical and functional results of pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) with peeling of the internal limiting membrane (ILM), membrane blue staining and subsequent expansile gas tamponade (perfluoropropane) in the treatment of idiopathic macular hole (IMH).
Material and methods: The retrospective analysis consisted of 100 eyes of a total of 100 patients (61 women and 39 men) with IMH, operated on at the Department of Ophthalmology of the Slovak Medical University and University Hospital Bratislava from 1 January 2021 to 1 January 2024, using 25-gauge PPV with ILM peeling and perfluoropropane tamponade (C3F8) of 15% concentration. After surgery, the patients were required to remain in a face-down position for at least one week. Best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), minimal linear diameter (MLD) on optic coherence tomography, macular hole closure type and occurrence of complications were evaluated. The obtained results were expressed with the use of arithmetic averages and displayed in graphs.
Results: Primary closure of macular hole was achieved in 93 patients (93%). The most frequently occurring type of closure was 1A. After surgery, the BCVA of all patients improved, from an average value of 0.101 preoperatively to 0.300 one year after surgery. In all groups of patients (regardless of the size of the macular hole before surgery), during the one-year follow-up period there was a gradual increase in BCVA with its stabilization by 6 months. The main factors that influenced postoperative BCVA were the preoperative values of MLD and BCVA.
Conclusion: PPV with ILM peeling and perfluoropropane tamponade is an effective treatment for idiopathic macular holes with a success rate of more than 90%. This surgical procedure, associated with a relatively low number of complications, brings patients a definite improvement of BCVA.